Largest therapy service 100% online
Better4U is a global therapy service designed to provide therapy that is personally tailored to fit your needs, available anytime and anywhere.
- Vetted therapist
- Easy process
- 100% confidential



Congratulations
You have an upcoming session.

4
KSessions Delivered
3
KRepeat Clients
30
+Corporate Partners
100
%Confidential

What type of therapy are you looking for?
How Online Therapy Works
Get matched to the best therapist for you
Answer a few questions to find a licensed therapist who fits your needs and preferences. Tap into the largest network of licensed providers.


Communicate your way
Talk to your therapist however you feel comfortable — text, chat, phone, or video.
Therapy when you need it
You can message your therapist at anytime, from anywhere. You also get to schedule live sessions when it's convenient for you, and can connect from any mobile device or computer.
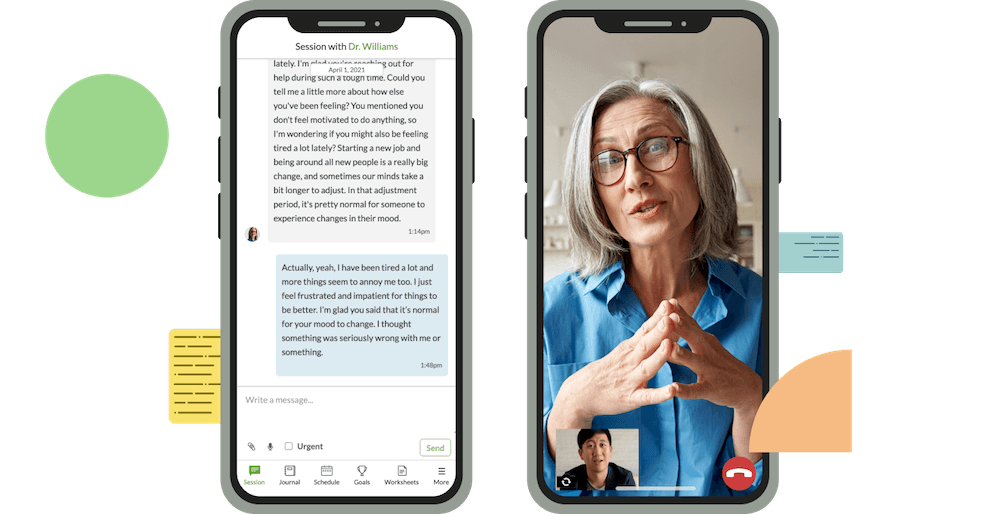
Professional, licensed, and vetted therapists who you can trust
Tap into the world's largest network of licensed, accredited, and experienced therapists who can help you with a range of issues including depression, anxiety, relationships, trauma, grief, and more. With our therapists, you get the same professionalism and quality you would expect from an in-office therapist, but with the ability to communicate when and how you want.










